Thank you for your interest in the Underground Railroad in Oakland County Project, a multi-community public history project to research and provide access to evidence-based local Underground Railroad history. We’re glad you’re here.
This website is a work in progress, with some information from our displays not yet presented on the site. Watch for updates as we complete this important part of our project, with more details, links to sources, and other information.
We’re serious about sources! Our goal is to provide you with complete information so you may consult original documents and digitized materials for yourself. We ask that you recognize the efforts of our researchers and their dedication by citing this website and/or our ‘Underground Railroad in Oakland County’ public history project if you use it in your work. Thank you.
Content Warning: Please note–objects and content on this website reflect the era and culture in which they were created. It is our mission to preserve historical records and make them available to the public. As such, they may contain potentially objectionable content that reflects outdated, biased, offensive, or graphic language, attitudes, opinions, or images that are preserved for historical context, accuracy, or significance, and not for any endorsement of such views or events.

If you would like to learn more, please feel free to reach out to Underground Railroad in Oakland County Project Director Leslie Pielack at the Birmingham Museum, lpielack@bhamgov.org. or 248-530-1928. This project is funded in part by Michigan Humanities, an affiliate of the National Endowment for the Humanties.
Oakland County’s Role in the Anti-Slavery Movement, 1830-1860
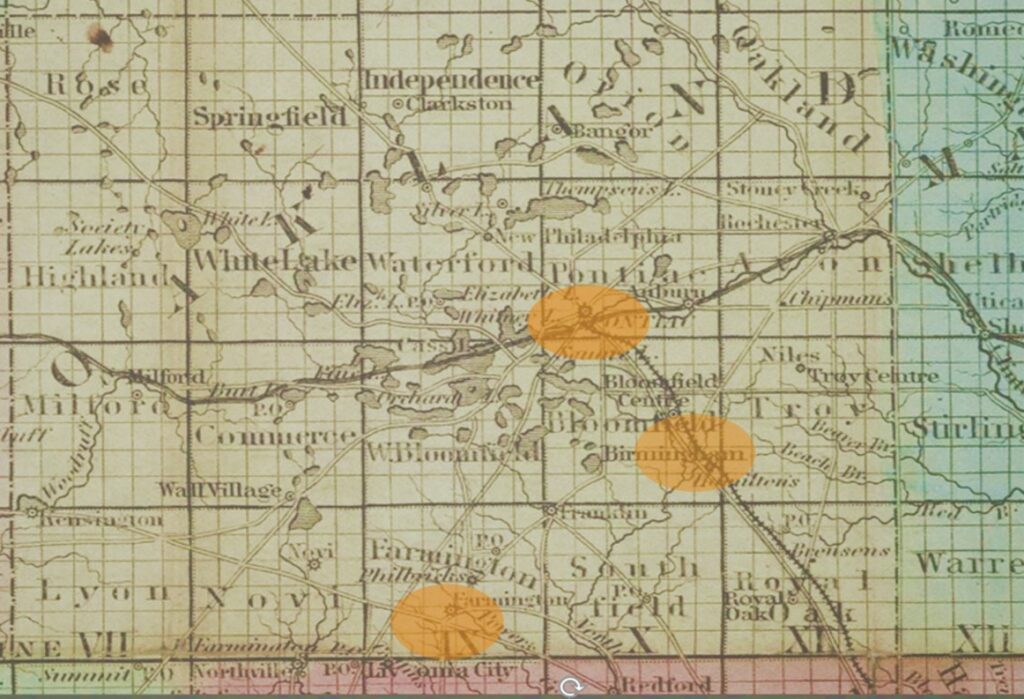
Before 1850: Central Role of Pontiac/Birmingham/Farmington
•Early/influential settlements with similar political, cultural, and religious interests
Closely involved in state and county efforts to establish policy and rule of law
•Were active in abolitionist efforts
•Were conveniently located on major roads that made it easier to maintain relationships, send messages, and meet in person
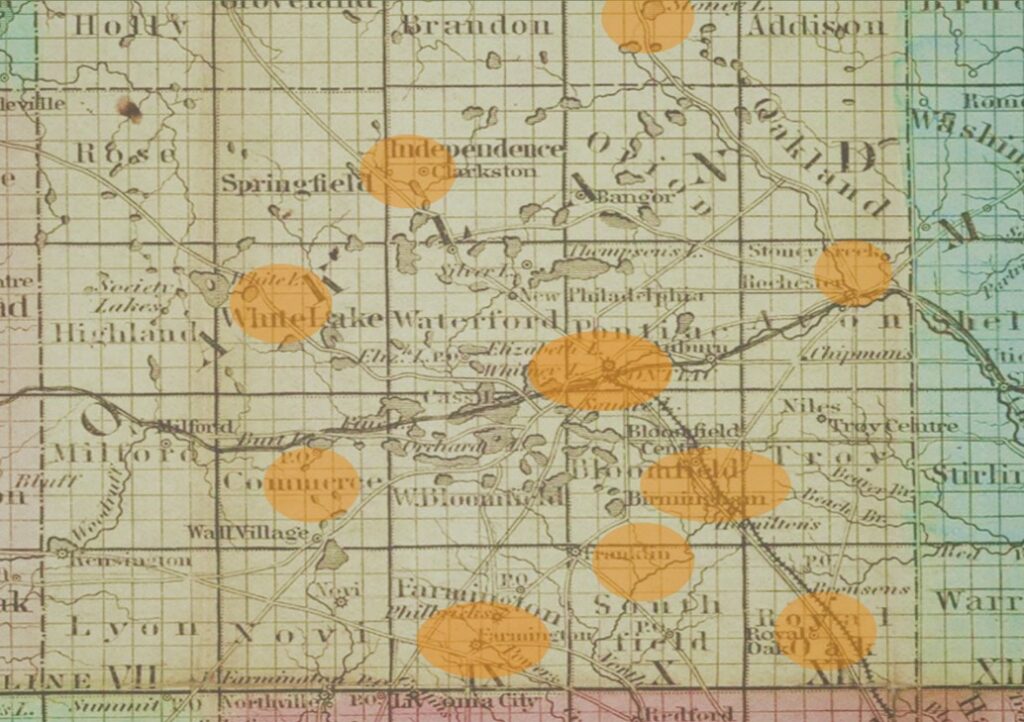
After 1850: Fanning Out and Going “Underground”
•The 1850 Fugitive Slave Act was designed to appease slave states. Freedom seekers could now be detained without proof and re-enslaved, even in free states. Those helping them could be arrested and subject to jail and heavy fines.
•Bounty hunters from the South came into Michigan looking for escapees, who now had to cross the Canadian border to be safe.
•To avoid bounty hunters in Detroit, the Underground Railroad network fanned out into Oakland County to move freedom seekers north to Lapeer, then Port Huron, and then to Canada.
Above map graphics by Leslie Pielack, ©Birmingham Museum. (After Farmer, Silas, “Map of the state of Michigan and the surrounding country exhibiting the sections and the latest surveys / compiled from authentic sources by John Farmer.” (1849). In the digital collection UM Clark Library Maps. https://quod.lib.umich.edu/c/clark1ic/x-000080675/39015091880008. University of Michigan Library Digital Collections. Accessed October 03, 2024.
